Room Correction
What is Room Correction?
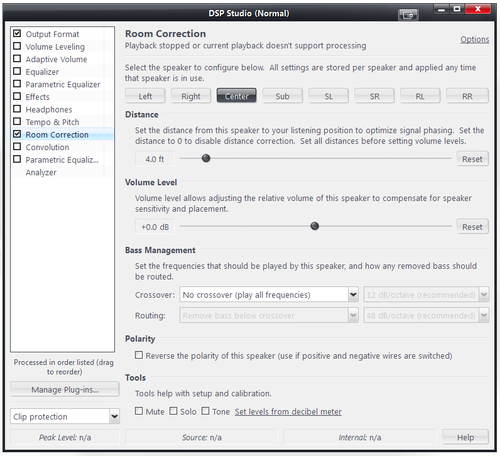
Media Center's DSP Studio provides a "Room Correction" module which enables Media Center to behave in a similar fashion to a home theater AV receiver. It allows you to:
- configure a surround sound system which has speakers are different distances to the main listening position
- apply per speaker gain trims to account for speakers that have different sensitivities
- mark speakers as "small" or "large", i.e. implement bass management which routes low frequency content to your subwoofer
Setup Instructions
Enable the Module
Open the DSP Studio, click on Room Correction and enable it by checking the box next to it.
Position the Module
The effect of the room correction module can overlap with the Parametric Equalizer and Convolution blocks so therefore we have to make sure the module is in the correct position in the signal chain. How to do this is described in [DSP#Ordering DSPs].
The functional overlap occurs because this module can:
- apply a delay to each channel
- apply a gain adjustment to each channel
- apply low and high pass filters the specified channels
One common approach is to list DSP blocks in the following order:
- Parametric Equalizer
- Room Correction
- Convolution
- Parametric Equalizer 2
This allows the 1st PEQ block to affect the input (source) channels which can be useful when applying personal preferences to the source content, for example EQ. Room Correction comes next in order to convert the source content to physical output channels. Convolution (optional) and PEQ2 follow which enables further equalisation for the room setup. This can include copying the subwoofer channel to additional output channels and applying independent EQ schemes to achieve a better end result.
Distance
This section applies if your speakers are physically located at different distances to the main listening position. To set this, for each speaker:
- click the named speaker button
- measure the physical distance from the main listening position to the speaker
- move the slider to measured distance
Distance and Subwoofers
Modern commercial subwoofers often contain DSP functionality built into the amplifier. This is used to provide features like PEQ and room correction. SVS are one example of a manufacturer that includes such functionality in their devices, for example https://www.svsound.com/blogs/svs/75346755-understanding-dsp
Such functionality will always add latency to the signal chain which has the effect of increasing the apparent distance to the subwoofer.
In these cases the physical distance may result in a lack of output around the crossover frequency. There are various ways to tackle this problem:
- ask the manufacturer how much delay is added by their device
- if you have a microphone
- measure the actual delay (e.g. using Room EQ Wizard)
- use the "sub distance tweak" (i.e. use an RTA and measure the combined response, adjust distance to achieve most SPL through the crossover range)
- guess and add ~2ft to the measured distance
Volume Level
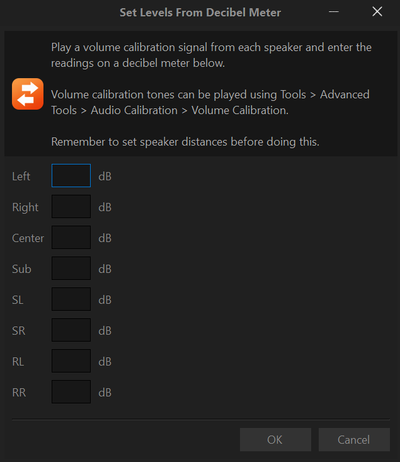
Using an SPL Meter
This is a simple and reliable way to get the levels right. To do this:
- click the "Set levels from decibel meter" link at the bottom of the page
- follow the instructions on the page to play the test tones
- hold the SPL meter at the listening position & measure each speaker in turn
- enter the measured SPL in dB into the form
- Click OK, the level meters will now be set for each speaker measured
By Ear
Use Tools > Advanced Tools > Audio Calibration > Volume Calibration to play band limited pink noise through each speaker in turn. Cycle back and forth through the channels, adjusting the volume sliders as you go until you perceive each speaker as playing at the same volume.
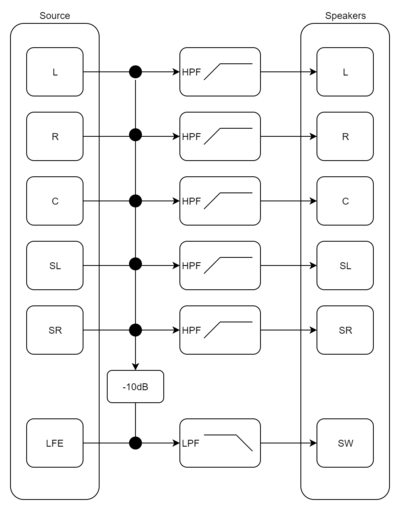
Bass Management
This section allows you to route low frequency content to the subwoofer channel while maintaining the correct levels with respect to the LFE channel.
NB: See Editing the Bass Management Diagram for details on how to update this diagram.
Alternatives to Room Correction
The functionality in the room correction module can be replaced by:
- using [Parametric Equalizer#Delay] to account for different distances per speaker
- using [Parametric Equalizer#Mixing], pass filters and pass filters to perform bass management
- performing all such functions via Convolution