WASAPI: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
WASAPI support was first added to Media Center 13. Media Center 15 added event style WASAPI support, and MC 18 made this the default. |
WASAPI support was first added to Media Center 13. Media Center 15 added event style WASAPI support, and MC 18 made this the default. |
||
== WASAPI |
== WASAPI Device Settings == |
||
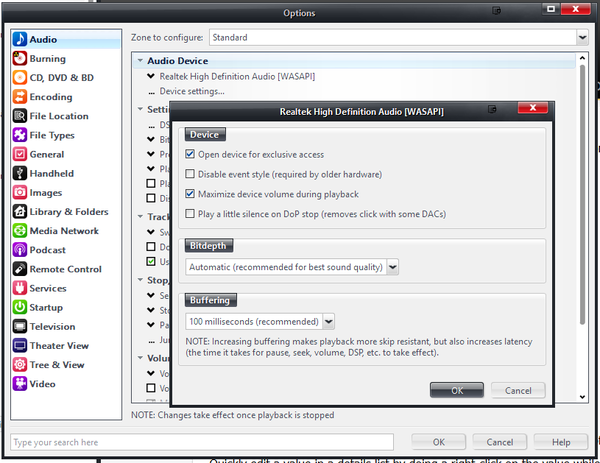
You can access WASAPI |
You can access WASAPI's Device Settings in Media Center via: |
||
<span style="color:#8B4513">Tools > Options > Audio > Audio Device > Device settings</span> |
<span style="color:#8B4513">Tools > Options > Audio > Audio Device > Device settings</span> |
||
Revision as of 05:25, 17 April 2014
- See also: Error: Template must be given at least one article name
The Windows Audio Session API (WASAPI) is Microsoft's most modern method for talking with audio devices. It is available in Windows Vista, Windows 7, and later versions of Windows. It allows delivering an unmodified bitstream to a sound device, and provides benefits similar to those provided by ASIO drivers. One of the other main benefits of WASAPI is that it provides applications with exclusive access to audio devices, bypassing the system mixer, default settings, and any typically any effects provided by the audio driver. WASAPI is the recommended Audio Output Mode for Windows unless your audio device has a well-behaved ASIO driver, and it effectively replaces all legacy output modes including Kernel Streaming and Direct Sound.
WASAPI support was first added to Media Center 13. Media Center 15 added event style WASAPI support, and MC 18 made this the default.
WASAPI Device Settings
You can access WASAPI's Device Settings in Media Center via: Tools > Options > Audio > Audio Device > Device settings
From here you can:
- Enable Exclusive access of the audio device.
- Disable WASAPI Event Style for supporting older hardware.
- Set Media Center to automatically maximize the audio device's system volume control during playback.
- Alter Buffering settings if needed to deal with troublesome hardware or drivers.
- Enable the Play a little silence option which can help prevent clicks and pops when starting and stopping playback that occurs on some audio devices